8.8. Service: VES Event Listener 5.4.1
Table of Contents
8.9. Introduction
This document describes the RESTful interface for the VES (Virtual function Event Streaming) Event Listener. The VES Event Listener is capable of receiving any event sent in the VES Common Event Format. The Common Event Format is a JSON structure consisting of a required Common Event Header Block accompanied by zero or more event domain blocks. A JSON Schema of the VES Common Event Format is provided in Section 4 of this document.
It should be understood that events are well structured packages of information, identified by an eventName, which are asynchronously communicated to subscribers who are interested in the eventName. Events can convey measurements, faults, syslogs, threshold crossing alerts and others types of information. Events are simply a way of communicating well-structured packages of information to one or more instances of an Event Listener service.
This document describes a RESTful connectionless push event listener that is capable of receiving single events or batches of events in the Common Event Format. In future, additional documents may describe other transports which make use of persistent TCP connections for high volumes of streaming events.
8.10. Event Registration
All events must be compliant with the common event format, but specific events identified by their eventNames, may require that certain fields, which are optional in the common event format, be present when they are published. For example, a specific eventName may require that specific name-value pairs be present in the extensible structures provided within the Common Event Format.
Events are registered using an extensible YAML format (defined in a separate document), which specifies, for each eventName, the fields that are required, what field values may be sent, and any special handling that should be performed on those eventNames.
8.11. Naming Standards for eventName
To prevent naming collisions, eventNames sent as part of the commonEventHeader, should conform to the following naming convention designed to summarize the purpose and type of the event, and to ensure the uniqueness of the eventName:
{DomainAbbreviation}_{SdcModel or ApplicationPlatform}_{DescriptionOfInfoBeingConveyed}
Domain abbreviations are derived from the ‘domain’ field in the commonEventHeader, as specified below: - ‘Fault’for the fault domain - ‘Heartbeat’for the heartbeat domain - ‘Mfvs’for the measurementsForVfScaling domain - ‘MobileFlow’for the mobileFlow domain - ‘Other’for the other domain - ‘SipSignaling’for the sipSignaling domain - ‘StateChange’for the stateChange domain - ‘Syslog’for the syslog domain - ‘Tca’for the thresholdCrossingAlert domain - ‘voiceQuality’for the voiceQuality domain
SDC (the ONAP Service Design and Creation environment) defines and catalogs specific services, VNFs, VF modules and other entities, which are generically referred to as ‘SDC models’. The SDC model that an event is associated with should be indicated in the second subfield within the eventName. If the event is not associated with an Sdc model but is instead being generated by an application platform like SO, then a string identifying the Application Platform may be used instead. In either case, all subfield names should be converted to camel case format (with no spaces, hyphens or underscores).
The final subfield of the eventName name should describe, in a compact camel case format (with no spaces, hyphens or underscores), the specific information being conveyed by the event. In some cases, this final subfield will not be required (e.g., in the case of Heartbeats or in the case of an event source which, for a domain like syslog, defines only one eventName to support it):
Examples of eventNames following the naming standards are provided below:
Fault_MobileCallRecording_PilotNumberPoolExhaustion
Heartbeat_vIsbcMmc
Other_WanBonding_InstantiationPart1Complete
Syslog_vDbe
Tca_vDbe_CpuThresholdExceeded
Other_SO_InstantiationPhase1Complete
Any questions about the naming of eventNames should be resolved as part of service and resource onboarding to the ONAP Service Design and Creation environment (i.e., SDC).
8.12. Support for Protocols Other Than HTTPS
This API specification describes an HTTPS RESTful interface using the JSON content-type.
Alternative specifications may be provided in future using Websockets, which would establish a permanent TCP socket, or Apache Avro which provides a binary format over an RPC protocol to be defined. Both would leverage the JSON schema provided in this document.
8.13. Versioning
Three types of version numbers supported by this specification:
The API specification itself is versioned. Going forward, the major number of the specification version will be incremented whenever any change could break an existing client (e.g., a field name is deleted or changed). All other changes to the spec (e.g., a field name is added or text changes are made to the specification itself) will increment only the minor number. Note that the major number appears in REST resource URLs as v# (where ‘#’is the major number).
The JSON schema is versioned. Going forward, the major number of the JSON schema will be incremented whenever any change could break an existing client (e.g., a field name is deleted or changed). All other changes to the schema (e.g., a field name is added or text changes are made to the field descriptions) will increment only the minor number.
The field blocks are versioned. Field blocks include the commonEventHeader and the domain blocks (e.g., the faultFields block). Going forward, the major number of each field block will be incremented whenever any change to that block could break an existing client (e.g., a field name is deleted or changed). All other changes to that block (e.g., a field name is added or text changes are made to the field descriptions) will increment only the minor number.
8.14. Security
Event sources must identify themselves to the VES Event Listener.
Event source credentials are passed using HTTP Basic Authentication.
Credentials must not be passed on the query string. Credentials must be sent in an Authorization header as follows:
The username and password are formed into one string as “username:password”
The resulting string is Base64 encoded to produce the encoded credential.
The encoded credential is communicated in the header after the string “Authorization: Basic “
Because the credentials are merely encoded but not encrypted, HTTPS (rather than HTTP) should be used. HTTPS will also encrypt and protect event contents.
Examples are provided below.
8.14.1. Sample Request and Response
8.15. Sample Request
POST /eventListener/v5 HTTPS/1.1 Authorization: Basic QWxhZGRpbjpvcGVuIHNlc2FtZQ== content-type: application/json content-length: 12345 { "event": { "commonEventHeader": { "version": 3.0, "domain": "heartbeat", "eventName": "Heartbeat\_vIsbcMmc", "eventId": "ab305d54-85b4-a31b-7db2fb6b9e546015", "sequence": 0, "priority": "Normal", "reportingEntityId": "cc305d54-75b4-431badb2eb6b9e541234", "reportingEntityName": "EricssonOamVf", "sourceId": "de305d54-75b4-431b-adb2-eb6b9e546014", "sourceName": "ibcx0001vm002ssc001", "nfNamingCode": "ibcx", "nfcNamingCode": "ssc", "startEpochMicrosec": 1413378172000000, "lastEpochMicrosec": 1413378172000000 } } }
8.16. Sample Success Response
HTTPS/1.1 202 Accepted
REST resources are defined with respect to a ServerRoot:
ServerRoot = /{optionalRoutingPath}
The resource structure is provided below:
{ServerRoot}
|
|--- /eventListener/v{apiVersion}
|
|--- /eventBatch
Figure 1: REST Resource Structure
The {Domain} or FQDN above is typically provisioned into each eventsource when it is instantiated. The {Port} above is typically 8443.
A JSON schema describing the Common Event Format is provided below and is reproduced in the tables that follow.
8.17. Common Event Datatypes
8.17.1. Common Event Datatypes
8.18. Datatype: event
The event datatype consists of the following fields which constitute the ‘root level’of the common event format:
Field |
Type |
Required? |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|
commonEventHeader |
commonEventHeader |
Yes |
Fields common to all events |
faultFields |
faultFields |
No |
Fields specific to fault events |
heartbeatFields |
heartbeatFields |
No |
Fields specific to heartbeat events |
measurementsForVfScalingFields |
measurementsForVfScalingFields |
No |
Fields specific to measurementsForVfScaling events |
mobileFlowFields |
mobileFlowFields |
No |
Fields specific to mobility flow events |
otherFields |
otherFields |
No |
Fields specific to other types of events |
sipSignalingFields |
sipSignalingFields |
No |
Fields specific to sipSignaling events |
stateChangeFields |
stateChangeFields |
No |
Fields specific to state change events |
syslogFields |
syslogFields |
No |
Fields specific to syslog events |
thresholdCrossingAlertFields |
thresholdCrossingAlertFields |
No |
Fields specific to threshold crossing alert events |
voiceQualityFields |
voiceQualityFields |
No |
Fields specific to voiceQuality events |
8.19. Datatype: eventList
The eventList datatype consists of the following fields:
Field |
Type |
Required? |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|
eventList |
event [ ] |
Yes |
Array of events |
8.20. Datatype: field
The field datatype consists of the following fields:
Field |
Type |
Required? |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|
name |
string |
Yes |
Name of the field |
value |
string |
Yes |
Value of the named field |
8.21. Datatype: jsonObject
The jsonObject datatype provides a json object schema, name and other meta-information along with one or more object instances that conform to the schema:
Field |
Type |
Required? |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|
objectInstances |
JsonObjectInstance [ ] |
Yes |
Contains one or more instances of the json object |
objectName |
string |
Yes |
Name of the json object |
objectSchema |
string |
No |
json schema for the object |
objectSchemaUrl |
string |
No |
URL to the json schema for the object |
nfSubscribedObjectName |
string |
No |
Name of the object associated with the nfSubscriptionId |
nfSubscriptionId |
string |
No |
Identifies an openConfig telemetry subscription on a network function, which configures the network function to send complex object data associated with the jsonObject |
8.22. Datatype: jsonObjectInstance
The jsonObjectInstance datatype provides meta-information about an instance of a jsonObject along with the actual object instance:
Field |
Type |
Required? |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|
objectInstance |
object |
Yes |
Contains an instance conforming to the jsonObject schema |
objectInstanceEpochMicrosec |
number |
No |
the unix time, aka epoch time, associated with this objectInstance–as microseconds elapsed since 1 Jan 1970 not including leap seconds |
objectKeys |
key [ ] |
No |
An ordered set of keys that identifies this particular instance of jsonObject (e.g., that places it in a hierarchy) |
8.23. Datatype: key
The key datatype is a tuple which provides the name of a key along with its value and relative order; it consists of the following fields:
Field |
Type |
Required? |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|
keyName |
string |
Yes |
Name of the key |
keyOrder |
Integer |
No |
Relative sequence or order of the key (with respect to other keys) |
keyValue |
string |
No |
Value of the key |
8.24. Datatype: namedArrayOfFields
The namedArrayOfFields datatype is an array of name value pairs along with a name for the array; it consists of the following fields:
Field |
Type |
Required? |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|
name |
string |
Yes |
Name for the array of name-value pairs |
arrayOfFields |
field [ ] |
Yes |
Name-value pairs |
8.25. Datatype: requestError
The requestError datatype defines the standard request error data structure:
Field |
Type |
Required? |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|
messageId |
string |
Yes |
Unique message identifier of the format ‘ABCnnnn’where ‘ABC’is either ‘SVC’for Service Exceptions or ‘POL’for Policy Exception. Exception numbers may be in the range of 0001 to 9999 where 0001 to 2999 are defined by OMA (see section 5.1) and 3000-9999 are available and undefined. |
text |
string |
Yes |
Message text, with replacement variables marked with %n, where n is an index into the list of <variables> elements, starting at 1 |
url |
string |
No |
Hyperlink to a detailed error resource e.g., an HTML page for browser user agents |
variables |
string |
No |
List of zero or more strings that represent the contents of the variables used by the message text |
8.26. Datatype: vendorVnfNameFields
The vendorVnfNameFields provides vendor, vnf and vfModule identifying information:
Field |
Type |
Required? |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|
vendorName |
string |
Yes |
VNF vendor name |
vfModuleName |
string |
No |
The Sdc vfModuleName for the vfModule generating the event |
vnfName |
string |
No |
The Sdc modelName for the VNF generating the event |
8.26.1. ‘Common Event Header’Datatypes
8.27. Datatype: commonEventHeader
The commonEventHeader datatype consists of the following fields common to all events:
Field |
Type |
Required? |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|
version |
number |
Yes |
Version of the event header (currently: 3.0) |
eventName |
string |
Yes |
Unique event name (see section 1 for more information) |
domain |
string |
Yes |
Event domain enumeration: ‘fault’, ‘heartbeat’, ‘measurementsForVfScaling’, ‘mobileFlow’, ‘other’, ‘sipSignaling’, ‘stateChange’, ‘syslog’, ‘thresholdCrossingAlert’, ‘voiceQuality’ |
eventId |
string |
Yes |
Event key that is unique to the event source |
eventType |
string |
No |
For example: ‘applicationVnf’, ‘guestOS’, ‘hostOS’, ‘platform’ |
nfcNamingCode |
string |
No |
Network function component type: 3 characters (aligned with vfc naming standards) |
nfNamingCode |
string |
No |
Network function type: 4 characters (aligned with vnf naming standards) |
sourceId |
string |
No |
UUID identifying the entity experiencing the event issue (note: the AT&T internal enrichment process shall ensure that this field is populated) |
sourceName |
string |
Yes |
Name of the entity experiencing the event issue |
reportingEntityId |
string |
No |
UUID identifying the entity reporting the event, for example an OAM VM (note: the AT&T internal enrichment process shall ensure that this field is populated) |
reportingEntityName |
string |
Yes |
Name of the entity reporting the event, for example, an EMS name. May be the same as the sourceName. For synthetic events generated by DCAE, it is the name of the app generating the event. |
priority |
string |
Yes |
Processing priority enumeration: ‘High’, ‘Medium’, ‘Normal’, ‘Low’ |
startEpochMicrosec |
number |
Yes |
the earliest unix time aka epoch time associated with the event from any component–as microseconds elapsed since 1 Jan 1970 not including leap seconds |
lastEpochMicrosec |
number |
Yes |
the latest unix time aka epoch time associated with the event from any component–as microseconds elapsed since 1 Jan 1970 not including leap seconds |
sequence |
integer |
Yes |
Ordering of events communicated by an event source instance (or 0 if not needed) |
internalHeader Fields |
internalHeader Fields |
No |
Fields (not supplied by event sources) that the VES Event Listener service can use to enrich the event if needed for efficient internal processing. This is an empty object which is intended to be defined separately by each provider implementing the VES Event Listener. |
8.28. Datatype: internalHeaderFields
The internalHeaderFields datatype is an undefined object which can contain arbitrarily complex JSON structures. It is intended to be defined separately by each provider implementing the VES Event Listener.
The fields in internalHeaderFields are not provided by any event source but instead are added by the VES Event Listener service itself as part of an event enrichment process necessary for efficient internal processing of events received by the VES Event Listener:
8.29. Technology Independent Datatypes
8.29.1. ‘Fault’Domain Datatypes
8.30. Datatype: faultFields
The faultFields datatype consists of the following fields:
Field |
Type |
Required? |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|
faultFieldsVersion |
number |
Yes |
Version of the faultFields block (currently: 2.0) |
eventSeverity |
string |
Yes |
Event severity enumeration: ‘CRITICAL’, ‘MAJOR’, ‘MINOR’, ‘WARNING’, ‘NORMAL’ |
eventSourceType |
string |
Yes |
Examples: ‘card’, ‘host’, ‘other’, ‘port’, ‘portThreshold’, ‘router’, ‘slotThreshold’, ‘switch’, ‘virtualMachine’, ‘virtualNetworkFunction’ |
eventCategory |
string |
No |
Event category, for example: ‘license’, ‘link’, ‘routing’, ‘security’, ‘signaling’ |
alarmCondition |
string |
Yes |
Alarm condition reported by the device (e.g., ‘tpLgCgiNotInConfig’) |
specificProblem |
string |
Yes |
Short description of the alarm or problem (e.g., ‘This event is sent when the LG is asked to perform a location for a CGI that is not in its configuration’) |
vfStatus |
string |
Yes |
Virtual function status enumeration: ‘Active’, ‘Idle’, ‘Preparing to terminate’, ‘Ready to terminate’, ‘Requesting Termination’ |
alarmInterfaceA |
string |
No |
Card, port, channel or interface name of the device generating the alarm |
alarmAdditional Information |
field [ ] |
No |
Additional alarm information (note: for SNMP mapping to VES, for name use OID of varbind, for value use incoming data for that varbind) |
8.30.1. ‘Heartbeat’Domain Datatypes
8.31. Datatype: heartbeatFields
The heartbeatFields datatype is an optional field block for fields specific to heartbeat events; it consists of the following fields:
Field |
Type |
Required? |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|
heartbeatFieldsVersion |
number |
Yes |
Version of the heartbeatFields block (currently: 1.0) |
additionalFields |
field [ ] |
No |
Additional expansion fields if needed |
heartbeatInterval |
Integer |
Yes |
Current heartbeatInterval in seconds |
8.31.1. Measurements For VF Scaling’Domain Datatypes
8.32. Datatype: codecsInUse
The codecsInUse datatype consists of the following fields describing the number of times an identified codec was used over the measurementInterval:
Field |
Type |
Required? |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|
codecIdentifer |
string |
Yes |
Description of the codec |
numberInUse |
integer |
Yes |
Number of such codecs in use |
8.33. Datatype: cpuUsage
The cpuUsage datatype defines the usage of an identifier CPU and consists of the following fields:
Field |
Type |
Required? |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|
cpuIdentifier |
string |
Yes |
CPU Identifier |
cpuIdle |
number |
No |
Percentage of CPU time spent in the idle task |
cpuUsageInterrupt |
number |
No |
Percentage of time spent servicing interrupts |
cpuUsageNice |
number |
No |
Percentage of time spent running user space processes that have been niced |
cpuUsageSoftIrq |
number |
No |
Percentage of time spent handling soft irq interrupts |
cpuUsageSteal |
number |
No |
Percentage of time spent in involuntary wait which is neither user, system or idle time and is effectively time that went missing |
cpuUsageSystem |
number |
No |
Percentage of time spent on system tasks running the kernel |
cpuUsageUser |
number |
No |
Percentage of time spent running un-niced user space processes |
cpuWait |
number |
No |
Percentage of CPU time spent waiting for I/O operations to complete |
percentUsage |
number |
Yes |
Aggregate cpu usage of the virtual machine on which the VNFC reporting the event is running |
8.34. Datatype: diskUsage
The diskUsage datatype defines the usage of a disk and consists of the following fields:
Field |
Type |
Required? |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|
diskIdentifier |
string |
Yes |
Disk Identifier |
diskIoTimeAvg |
number |
No |
Milliseconds spent doing input/output operations over 1 sec; treat this metric as a device load percentage where 1000ms matches 100% load; provide the average over the measurement interval |
diskIoTimeLast |
number |
No |
Milliseconds spent doing input/output operations over 1 sec; treat this metric as a device load percentage where 1000ms matches 100% load; provide the last value measurement within the measurement interval |
diskIoTimeMax |
number |
No |
Milliseconds spent doing input/output operations over 1 sec; treat this metric as a device load percentage where 1000ms matches 100% load; provide the maximum value measurement within the measurement interval |
diskIoTimeMin |
number |
No |
Milliseconds spent doing input/output operations over 1 sec; treat this metric as a device load percentage where 1000ms matches 100% load; provide the minimum value measurement within the measurement interval |
diskMergedReadAvg |
number |
No |
Number of logical read operations that were merged into physical read operations, e.g., two logical reads were served by one physical disk access; provide the average measurement within the measurement interval |
diskMergedReadLast |
number |
No |
Number of logical read operations that were merged into physical read operations, e.g., two logical reads were served by one physical disk access; provide the last value measurement within the measurement interval |
diskMergedReadMax |
number |
No |
Number of logical read operations that were merged into physical read operations, e.g., two logical reads were served by one physical disk access; provide the maximum value measurement within the measurement interval |
diskMergedReadMin |
number |
No |
Number of logical read operations that were merged into physical read operations, e.g., two logical reads were served by one physical disk access; provide the minimum value measurement within the measurement interval |
diskMergedWriteAvg |
number |
No |
Number of logical write operations that were merged into physical write operations, e.g., two logical writes were served by one physical disk access; provide the average measurement within the measurement interval |
diskMergedWriteLast |
number |
No |
Number of logical write operations that were merged into physical write operations, e.g., two logical writes were served by one physical disk access; provide the last value measurement within the measurement interval |
diskMergedWriteMax |
number |
No |
Number of logical write operations that were merged into physical write operations, e.g., two logical writes were served by one physical disk access; provide the maximum value measurement within the measurement interval |
diskMergedWriteMin |
number |
No |
Number of logical write operations that were merged into physical write operations, e.g., two logical writes were served by one physical disk access; provide the minimum value measurement within the measurement interval |
diskOctetsRead Avg |
number |
No |
Number of octets per second read from a disk or partition; provide the average measurement within the measurement interval |
diskOctetsRead Last |
number |
No |
Number of octets per second read from a disk or partition; provide the last measurement within the measurement interval |
diskOctetsRead Max |
number |
No |
Number of octets per second read from a disk or partition; provide the maximum measurement within the measurement interval |
diskOctetsRead Min |
number |
No |
Number of octets per second read from a disk or partition; provide the minimum measurement within the measurement interval |
diskOctetsWrite Avg |
number |
No |
Number of octets per second written to a disk or partition; provide the average measurement within the measurement interval |
diskOctetsWrite Last |
number |
No |
Number of octets per second written to a disk or partition; provide the last measurement within the measurement interval |
diskOctetsWriteMax |
number |
No |
Number of octets per second written to a disk or partition; provide the maximum measurement within the measurement interval |
diskOctetsWriteMin |
number |
No |
Number of octets per second written to a disk or partition; provide the minimum measurement within the measurement interval |
diskOpsReadAvg |
number |
No |
Number of read operations per second issued to the disk; provide the average measurement within the measurement interval |
diskOpsReadLast |
number |
No |
Number of read operations per second issued to the disk; provide the last measurement within the measurement interval |
diskOpsReadMax |
number |
No |
Number of read operations per second issued to the disk; provide the maximum measurement within the measurement interval |
diskOpsReadMin |
number |
No |
Number of read operations per second issued to the disk; provide the minimum measurement within the measurement interval |
diskOpsWriteAvg |
number |
No |
Number of write operations per second issued to the disk; provide the average measurement within the measurement interval |
diskOpsWriteLast |
number |
No |
Number of write operations per second issued to the disk; provide the last measurement within the measurement interval |
diskOpsWrite Max |
number |
No |
Number of write operations per second issued to the disk; provide the maximum measurement within the measurement interval |
diskOpsWriteMin |
number |
No |
Number of write operations per second issued to the disk; provide the minimum measurement within the measurement interval |
diskPendingOperationsAvg |
number |
No |
Queue size of pending I/O operations per second; provide the average measurement within the measurement interval |
diskPendingOperationsLast |
number |
No |
Queue size of pending I/O operations per second; provide the last measurement within the measurement interval |
diskPendingOperationsMax |
number |
No |
Queue size of pending I/O operations per second; provide the maximum measurement within the measurement interval |
diskPendingOperationsMin |
number |
No |
Queue size of pending I/O operations per second; provide the minimum measurement within the measurement interval |
diskTimeReadAvg |
number |
No |
Milliseconds a read operation took to complete; provide the average measurement within the measurement interval |
diskTimeRead Last |
number |
No |
Milliseconds a read operation took to complete; provide the last measurement within the measurement interval |
diskTimeRead Max |
number |
No |
Milliseconds a read operation took to complete; provide the maximum measurement within the measurement interval |
diskTimeRead Min |
number |
No |
Milliseconds a read operation took to complete; provide the minimum measurement within the measurement interval |
diskTimeWrite Avg |
number |
No |
Milliseconds a write operation took to complete; provide the average measurement within the measurement interval |
diskTimeWrite Last |
number |
No |
Milliseconds a write operation took to complete; provide the last measurement within the measurement interval |
diskTimeWrite Max |
number |
No |
Milliseconds a write operation took to complete; provide the maximum measurement within the measurement interval |
diskTimeWrite Min |
number |
No |
Milliseconds a write operation took to complete; provide the minimum measurement within the measurement interval |
8.35. Datatype: featuresInUse
The featuresInUse datatype consists of the following fields which describe the number of times an identified feature was used over the measurementInterval:
Field |
Type |
Required? |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|
featureIdentifer |
string |
Yes |
Description of the feature |
featureUtilization |
integer |
Yes |
Number of times the identified feature was used |
8.36. Datatype: filesystemUsage
The filesystemUsage datatype consists of the following fields:
Field |
Type |
Required? |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|
filesystemName |
string |
Yes |
File system name |
blockConfigured |
number |
Yes |
Configured block storage capacity in GB |
blockIops |
number |
Yes |
Block storage input-output operations per second |
blockUsed |
number |
Yes |
Used block storage capacity in GB |
ephemeralConfigured |
number |
Yes |
Configured ephemeral storage capacity in GB |
ephemeralIops |
number |
Yes |
Ephemeral storage input-output operations per second |
ephemeralUsed |
number |
Yes |
Used ephemeral storage capacity in GB |
8.37. Datatype: latencyBucketMeasure
The latencyBucketMeasure datatype consists of the following fields which describe the number of counts falling within a defined latency bucket:
Field |
Type |
Required? |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|
countsInTheBucket |
number |
Yes |
Number of counts falling within a defined latency bucket |
highEndOfLatencyBucket |
number |
No |
High end of bucket range (typically in ms) |
lowEndOfLatencyBucket |
number |
No |
Low end of bucket range (typically in ms) |
8.38. Datatype: measurementsForVfScalingFields
The measurementsForVfScalingFields datatype consists of the following fields:
Field |
Type |
Required? |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|
measurementsForVfScalingVersion |
number |
Yes |
Version of the measurementsForVfScalingFields block (currently: 2.0) |
additionalFields |
field [ ] |
No |
Additional measurement fields if needed |
additionalMeasurements |
namedArrayOfFields [ ] |
No |
Array of named name-value-pair arrays if needed |
additionalObjects |
jsonObject [ ] |
No |
Array of JSON objects described by name, schema and other meta-information, if needed |
codecUsageArray |
codecsInUse [] |
No |
Array of codecs in use |
concurrentSessions |
integer |
No |
Peak concurrent sessions for the VM or VNF (depending on the context) over the measurementInterval |
configuredEntities |
integer |
No |
Depending on the context over the measurementInterval: peak total number of users, subscribers, devices, adjacencies, etc., for the VM, or peak total number of subscribers, devices, etc., for the VNF |
cpuUsageArray |
cpuUsage [] |
No |
Usage of an array of CPUs |
diskUsageArray |
diskUsage [] |
No |
Usage of an array of disks |
featureUsageArray |
featuresInUse [] |
No |
Array of features in use |
filesystemUsageArray |
filesystemUsage [] |
No |
Filesystem usage of the VM on which the VNFC reporting the event is running |
latencyDistribution |
latencyBucketMeasure [ ] |
No |
Array of integers representing counts of requests whose latency in milliseconds falls within per-VNF configured ranges; where latency is the duration between a service request and its fulfillment. |
meanRequestLatency |
number |
No |
Mean seconds required to respond to each request for the VM on which the VNFC reporting the event is running |
measurementInterval |
number |
Yes |
Interval over which measurements are being reported in seconds |
memoryUsageArray |
memoryUsage [] |
No |
Memory usage of an array of VMs |
numberOfMediaPortsInUse |
integer |
No |
Number of media ports in use |
requestRate |
number |
No |
Peak rate of service requests per second to the VNF over the measurementInterval |
vnfcScalingMetric |
integer |
No |
Represents busy-ness of the VNF from 0 to 100 as reported by the VNFC |
vNicPerformanceArray |
vNicPerformance [ ] |
No |
Performance metrics of an array of virtual network interface cards |
8.39. Datatype: memoryUsage
The memoryUsage datatype defines the memory usage of a virtual machine and consists of the following fields:
Field |
Type |
Required? |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|
memoryBuffered |
number |
No |
Kibibytes of temporary storage for raw disk blocks |
memoryCached |
number |
No |
Kibibytes of memory used for cache |
memoryConfigured |
number |
No |
Kibibytes of memory configured in the virtual machine on which the VNFC reporting the event is running |
memoryFree |
number |
Yes |
Kibibytes of physical RAM left unused by the system |
memorySlabRecl |
number |
No |
The part of the slab that can be reclaimed such as caches measured in kibibytes |
memorySlabUnrecl |
number |
No |
The part of the slab that cannot be reclaimed even when lacking memory measure in kibibytes |
memoryUsed |
number |
Yes |
Total memory minus the sum of free, buffered, cached and slab memory measured in kibibytes |
vmIdentifier |
string |
Yes |
Virtual Machine identifier associated with the memory metrics |
8.40. Datatype: vNicPerformance
The vNicPerformance datatype consists of the following fields which describe the performance and errors of an of an identified virtual network interface card:
Field |
Type |
Required? |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|
receivedBroadcastPacketsAccumulated |
number |
No |
Cumulative count of broadcast packets received as read at the end of the measurement interval |
receivedBroadcastPacketsDelta |
number |
No |
Count of broadcast packets received within the measurement interval |
receivedDiscardedPacketsAccumulated |
number |
No |
Cumulative count of discarded packets received as read at the end of the measurement interval |
receivedDiscardedPacketsDelta |
number |
No |
Count of discarded packets received within the measurement interval |
receivedErrorPacketsAccumulated |
number |
No |
Cumulative count of error packets received as read at the end of the measurement interval |
receivedErrorPacketsDelta |
number |
No |
Count of error packets received within the measurement interval |
receivedMulticastPacketsAccumulated |
number |
No |
Cumulative count of multicast packets received as read at the end of the measurement interval |
receivedMulticastPacketsDelta |
number |
No |
Count of multicast packets received within the measurement interval |
receivedOctetsAccumulated |
number |
No |
Cumulative count of octets received as read at the end of the measurement interval |
receivedOctetsDelta |
number |
No |
Count of octets received within the measurement interval |
receivedTotalPacketsAccumulated |
number |
No |
Cumulative count of all packets received as read at the end of the measurement interval |
receivedTotalPacketsDelta |
number |
No |
Count of all packets received within the measurement interval |
receivedUnicastPacketsAccumulated |
number |
No |
Cumulative count of unicast packets received as read at the end of the measurement interval |
receivedUnicastPacketsDelta |
number |
No |
Count of unicast packets received within the measurement interval |
transmittedBroadcastPacketsAccumulated |
number |
No |
Cumulative count of broadcast packets transmitted as read at the end of the measurement interval |
transmittedBroadcastPacketsDelta |
number |
No |
Count of broadcast packets transmitted within the measurement interval |
transmittedDiscardedPacketsAccumulated |
number |
No |
Cumulative count of discarded packets transmitted as read at the end of the measurement interval |
transmittedDiscardedPacketsDelta |
number |
No |
Count of discarded packets transmitted within the measurement interval |
transmittedErrorPacketsAccumulated |
number |
No |
Cumulative count of error packets transmitted as read at the end of the measurement interval |
transmittedErrorPacketsDelta |
number |
No |
Count of error packets transmitted within the measurement interval |
transmittedMulticastPacketsAccumulated |
number |
No |
Cumulative count of multicast packets transmitted as read at the end of the measurement interval |
transmittedMulticastPacketsDelta |
number |
No |
Count of multicast packets transmitted within the measurement interval |
transmittedOctetsAccumulated |
number |
No |
Cumulative count of octets transmitted as read at the end of the measurement interval |
transmittedOctetsDelta |
number |
No |
Count of octets transmitted within the measurement interval |
transmittedTotalPacketsAccumulated |
number |
No |
Cumulative count of all packets transmitted as read at the end of the measurement interval |
transmittedTotalPacketsDelta |
number |
No |
Count of all packets transmitted within the measurement interval |
transmittedUnicastPacketsAccumulated |
number |
No |
Cumulative count of unicast packets transmitted as read at the end of the measurement interval |
transmittedUnicastPacketsDelta |
number |
No |
Count of unicast packets transmitted within the measurement interval |
valuesAreSuspect |
string |
Yes |
Enumeration: ‘true’or ‘false’. If ‘true’then the vNicPerformance values are likely inaccurate due to counter overflow or other condtions. |
vNicIdentifier |
string |
Yes |
vNic identification |
8.40.1. ‘Other’Domain Datatypes
8.41. Datatype: otherFields
The otherFields datatype defines fields for events belonging to the ‘other’ domain of the commonEventHeader domain enumeration; it consists of the following fields:
Field |
Type |
Required? |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|
otherFieldsVersion |
number |
Yes |
Version of the otherFields block (currently: 1.1) |
hashOfNameValuePairArrays |
namedArrayOfFields [ ] |
No |
Array of named name-value-pair arrays |
jsonObjects |
jsonObject [ ] |
No |
Array of JSON objects described by name, schema and other meta-information |
nameValuePairs |
field [ ] |
No |
Array of name-value pairs |
8.41.1. ‘State Change’Domain Datatypes
8.42. Datatype: stateChangeFields
The stateChangeFields datatype consists of the following fields:
Field |
Type |
Required? |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|
stateChangeFieldsVersion |
number |
Yes |
Version of the stateChangeFields block (currently: 2.0) |
additionalFields |
field [ ] |
No |
Additional stateChange fields if needed |
newState |
string |
Yes |
New state of the entity: ‘inService’, ‘maintenance’, ‘outOfService’ |
oldState |
string |
Yes |
Previous state of the entity: ‘inService’, ‘maintenance’, ‘outOfService’ |
stateInterface |
string |
Yes |
Card or port name of the entity that changed state |
8.42.1. ‘Syslog’Domain Datatypes
8.43. Datatype: syslogFields
The syslogFields datatype consists of the following fields:
Field |
Type |
Required? |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|
syslogFieldsVersion |
number |
Yes |
Version of the syslogFields block (currently: 3.0) |
additionalFields |
string |
No |
Additional syslog fields if needed, provided as name=value delimited by a pipe |
eventSourceHost |
string |
No |
Hostname of the device |
eventSourceType |
string |
Yes |
Examples: ‘other’, ‘router’, ‘switch’, ‘host’, ‘card’, ‘port’, ‘slotThreshold’, ‘portThreshold’, ‘virtualMachine’, ‘virtualNetworkFunction’ |
syslogFacility |
integer |
No |
Numeric code from 0 to 23 for facility: 0 kernel messages 1 user-level messages 2 mail system 3 system daemons 4 security/authorization messages 5 messages generated internally by syslogd 6 line printer subsystem 7 network news subsystem 8 UUCP subsystem 9 clock daemon 10 security/authorization messages 11 FTP daemon 12 NTP subsystem 13 log audit 14 log alert 15 clock daemon (note 2) 16 local use 0 (local0) 17 local use 1 (local1) 18 local use 2 (local2) 19 local use 3 (local3) 20 local use 4 (local4) 21 local use 5 (local5) 22 local use 6 (local6) 23 local use 7 (local7 ) |
syslogMsg |
string |
Yes |
Syslog message |
syslogPri |
integer |
No |
0-192 Combined Severity and Facility |
syslogProc |
string |
No |
Identifies the application that originated the message |
syslogProcId |
number |
No |
A change in the value of this field indicates a discontinuity in syslog reporting |
syslogSData |
string |
No |
Syslog structured data consisting of a structured data Id followed by a set of key value pairs (see below for an example) **Note: SD-ID may not be present if syslogSdId is populated |
syslogSdId |
string |
No |
0-32 char in format name@number, i.e., ourSDID@32473 |
syslogSev |
string |
No |
Level-of-severity enumeration in quotes below: ‘Emergency’: system is unusable ‘Alert’: action must be taken immediately ‘Critical’: critical conditions ‘Error’: error conditions ‘Warning’: warning conditions ‘Notice’: normal but significant condition ‘Info’: Informational: informational messages ‘Debug’: debug-level messages |
syslogTag |
string |
Yes |
MsgId indicating the type of message such as ‘TCPOUT’or ‘TCPIN’; ‘NILVALUE’should be used when no other value can be provided |
syslogVer |
number |
No |
IANA assigned version of the syslog protocol specification (typically ‘1’) |
Example of syslogSData:
STRUCTURED-DATA = NILVALUE / 1*SD-ELEMENT
SD-ELEMENT = “[” SD-ID *(SP SD-PARAM) “]”
SD-PARAM = PARAM-NAME “=” %d34 PARAM-VALUE %d34
SD-ID = SD-NAME
PARAM-NAME = SD-NAME
PARAM-VALUE = UTF-8-STRING ; characters ‘”’, ‘\’ and
; ‘]’ MUST be escaped.
SD-NAME = 1*32PRINTUSASCII
; except ‘=’, SP, ‘]’, %d34 (“)
8.43.1. ‘Threshold Crossing Alert’Domain Datatypes
8.44. Datatype: counter
The counter datatype consists of the following fields:
Field |
Type |
Required? |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|
name |
string |
Yes |
Name of the counter |
value |
string |
Yes |
Current value of the counter |
threshholdCrossed |
string |
Yes |
Last threshold that was crossed |
criticality |
string |
Yes |
Enumeration: ‘CRIT’, ‘MAJ’ |
8.44.1. Datatype: thresholdCrossingAlertFields
The thresholdCrossingAlertFields datatype consists of the following fields:
Field |
Type |
Required? |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|
thresholdCrossing FieldsVersion |
number |
Yes |
Version of the thresholdCrossingAlertFields block (currently: 2.0) |
additionalFields |
field [ ] |
No |
Additional threshold crossing alert fields if needed |
additionalParameters |
counter [ ] |
Yes |
Array of performance counters |
alertAction |
string |
Yes |
Enumeration: ‘SET’, ‘CONT’, ‘CLEAR’ |
alertDescription |
string |
Yes |
Unique short alert description (e.g., NE-CPUMEM) |
alertType |
string |
Yes |
Enumeration: ‘CARD-ANOMALY’, ‘INTERFACE-ANOMALY’, ELEMENT-ANOMALY’, ‘SERVICE-ANOMALY’ |
alertValue |
string |
No |
Calculated API value (if applicable) |
associatedAlertIdList |
string [ ] |
No |
List of eventIds associated with the event being reported |
collectionTimestamp |
string |
Yes |
Time when the performance collector picked up the data; with RFC 2822 compliant format: ‘Sat, 13 Mar 2010 11:29:05 -0800’ |
dataCollector |
string |
No |
Specific performance collector instance used |
elementType |
string |
No |
Type of network element (internal AT&T field) |
eventSeverity |
string |
Yes |
Event severity or priority enumeration: ‘CRITICAL’, ‘MAJOR’, ‘MINOR’, ‘WARNING’, ‘NORMAL’ |
eventStartTimestamp |
string |
Yes |
Time closest to when the measurement was made; with RFC 2822 compliant format: ‘Sat, 13 Mar 2010 11:29:05 -0800’ |
interfaceName |
string |
No |
Physical or logical port or card (if applicable) |
networkService |
string |
No |
Network name (internal AT&T field) |
possibleRootCause |
string |
No |
Reserved for future use |
8.45. Technology Specific Datatypes
8.45.1. ‘Mobile Flow’ Domain Datatypes
8.46. Datatype: gtpPerFlowMetrics
The gtpPerFlowMetrics datatype consists of the following fields:
8.47. Datatype: mobileFlowFields
The mobileFlowFields datatype consists of the following fields:
Field |
Type |
Required? |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|
mobileFlowFieldsVersion |
number |
Yes |
Version of the mobileFlowFields block (currently: 2.0) |
additionalFields |
field [ ] |
No |
Additional mobileFlow fields if needed |
applicationType |
string |
No |
Application type inferred |
appProtocolType |
string |
No |
Application protocol |
appProtocolVersion |
string |
No |
Application version |
cid |
string |
No |
Cell Id |
connectionType |
string |
No |
Abbreviation referencing a 3GPP reference point e.g., S1-U, S11, etc |
ecgi |
string |
No |
Evolved Cell Global Id |
flowDirection |
string |
Yes |
Flow direction, indicating if the reporting node is the source of the flow or destination for the flow |
gtpPerFlowMetrics |
gtpPer FlowMetrics |
Yes |
Mobility GTP Protocol per flow metrics |
gtpProtocolType |
string |
No |
GTP protocol |
gtpVersion |
string |
No |
GTP protocol version |
httpHeader |
string |
No |
HTTP request header, if the flow connects to a node referenced by HTTP |
imei |
string |
No |
IMEI for the subscriber UE used in this flow, if the flow connects to a mobile device |
imsi |
string |
No |
IMSI for the subscriber UE used in this flow, if the flow connects to a mobile device |
ipProtocolType |
string |
Yes |
IP protocol type e.g., TCP, UDP, RTP… |
ipVersion |
string |
Yes |
IP protocol version e.g., IPv4, IPv6 |
lac |
string |
No |
Location area code |
mcc |
string |
No |
Mobile country code |
mnc |
string |
No |
Mobile network code |
msisdn |
string |
No |
MSISDN for the subscriber UE used in this flow, as an integer, if the flow connects to a mobile device |
otherEndpointIpAddress |
string |
Yes |
IP address for the other endpoint, as used for the flow being reported on |
otherEndpointPort |
integer |
Yes |
IP Port for the reporting entity, as used for the flow being reported on |
otherFunctionalRole |
string |
No |
Functional role of the other endpoint for the flow being reported on e.g., MME, S-GW, P-GW, PCRF… |
rac |
string |
No |
Routing area code |
radioAccessTechnology |
string |
No |
Radio Access Technology e.g., 2G, 3G, LTE |
reportingEndpointIpAddr |
string |
Yes |
IP address for the reporting entity, as used for the flow being reported on |
reportingEndpointPort |
integer |
Yes |
IP port for the reporting entity, as used for the flow being reported on |
sac |
string |
No |
Service area code |
samplingAlgorithm |
integer |
No |
Integer identifier for the sampling algorithm or rule being applied in calculating the flow metrics if metrics are calculated based on a sample of packets, or 0 if no sampling is applied |
tac |
string |
No |
Transport area code |
tunnelId |
string |
No |
Tunnel identifier |
vlanId |
string |
No |
VLAN identifier used by this flow |
8.47.1. ‘SipSignaling’Domain Datatypes
8.48. Datatype: sipSignalingFields
The sipSignalingFields datatype communicates information about sip signaling messages, parameters and signaling state; it consists of the following fields:
Field |
Type |
Required? |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|
sipSignalingFieldsVersion |
number |
Yes |
Version of the sipSignalingFields block (currently: 1.0) |
additionalInformation |
field [ ] |
No |
Additional sipSignaling fields |
compressedSip |
string |
No |
The full SIP request/response including headers and bodies |
correlator |
string |
Yes |
Constant across all events on this call |
localIpAddress |
string |
Yes |
IP address on VNF |
localPort |
string |
Yes |
Port on VNF |
remoteIpAddress |
string |
Yes |
IP address of peer endpoint |
remotePort |
string |
Yes |
Port of peer endpoint |
summarySip |
string |
No |
The SIP Method or Response (‘INVITE’, ‘200 OK’, ‘BYE’, etc) |
vendorVnfNameFields |
vendorVnfNameFields |
Yes |
Vendor, VNF and VfModule names |
8.48.1. ‘Voice Quality’Domain Datatypes
8.49. Datatype: endOfCallVqmSummaries
The endOfCallVqmSummaries datatype provides end of call voice quality metrics; it consists of the following fields:
Field |
Type |
Required? |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|
adjacencyName |
string |
Yes |
Adjacency name |
endpointDescription |
string |
Yes |
Enumeration: ‘Caller’, ‘Callee’ |
endpointJitter |
number |
No |
Endpoint jitter |
endpointRtpOctetsDiscarded |
number |
No |
Endpoint RTP octets discarded |
endpointRtpOctetsReceived |
number |
No |
Endpoint RTP octets received |
endpointRtpOctetsSent |
number |
No |
Endpoint RTP octets sent |
endpointRtpPacketsDiscarded |
number |
No |
Endpoint RTP packets discarded |
endpointRtpPacketsReceived |
number |
No |
Endpoint RTP packets received |
endpointRtpPacketsSent |
number |
No |
Endpoint RTP packets sent |
localJitter |
number |
No |
Local jitter |
localRtpOctetsDiscarded |
number |
No |
Local RTP octets discarded |
localRtpOctetsReceived |
number |
No |
Local RTP octets received |
localRtpOctetsSent |
number |
No |
Local RTP octets sent |
localRtpPacketsDiscarded |
number |
No |
Local RTP packets discarded |
localRtpPacketsReceived |
number |
No |
Local RTP packets received |
localRtpPacketsSent |
number |
No |
Local RTP packets sent |
mosCqe |
number |
No |
Decimal range from 1 to 5 (1 decimal place) |
packetsLost |
number |
No |
Packets lost |
packetLossPercent |
number |
No |
Calculated percentage packet loss based on endpoint RTP packets lost (as reported in RTCP) and local RTP packets sent. Direction is based on endpoint description (Caller, Callee). Decimal (2 decimal places) |
rFactor |
number |
No |
rFactor from 0 to 100 |
roundTripDelay |
number |
No |
Round trip delay in milliseconds |
8.50. Datatype: voiceQualityFields
The voiceQualityFields datatype provides statistics related to customer facing voice products; consists of the following fields:
Field |
Type |
Required? |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|
voiceQualityFieldsVersion |
number |
Yes |
Version of the voiceQualityFields block (currently: 1.0) |
additionalInformation |
field [ ] |
No |
Additional voice quality fields |
calleeSideCodec |
string |
Yes |
Callee codec for the call |
callerSideCodec |
string |
Yes |
Caller codec for the call |
correlator |
string |
Yes |
Constant across all events on this call |
endOfCallVqmSummaries |
endOfCallVqm Summaries |
No |
End of call voice quality metric summaries |
phoneNumber |
string |
No |
Phone number associated with the correlator |
midCallRtcp |
string |
Yes |
Base64 encoding of the binary RTCP data (excluding Eth/IP/UDP headers) |
vendorVnfNameFields |
vendorVnfNameFields |
Yes |
Vendor, VNF and VfModule names |
8.51. RESTful Web Services Exceptions
RESTful services generate and send exceptions to clients in response to invocation errors. Exceptions send HTTP status codes (specified later in this document for each operation). HTTP status codes may be followed by an optional JSON exception structure described below. Two types of exceptions may be defined: service exceptions and policy exceptions.
Field Name |
Data Type |
Required? |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|
messageId |
xs:string |
Yes |
Unique message identifier of the format ‘ABCnnnn’where ‘ABC’is either ‘SVC’for Service Exceptions or ‘POL’for Policy Exception. Exception numbers may be in the range of 0001 to 9999 where :
|
text |
xs:string |
Yes |
Message text, with replacement variables marked with %n, where n is an index into the list of <variables> elements, starting at 1 |
variables |
xs:string [0..unbounded] |
No |
List of zero or more strings that represent the contents of the variables used by the message text. |
url |
xs:anyUrl |
No |
Hyperlink to a detailed error resource (e.g., an HTML page for browser user agents). |
8.52. Service Exceptions
When a service is not able to process a request, and retrying the request with the same information will also result in a failure, and the issue is not related to a service policy issue, then the service will issue a fault using the service exception fault message. Examples of service exceptions include invalid input, lack of availability of a required resource or a processing error.
A service exception uses the letters ‘SVC’ at the beginning of the message identifier. ‘SVC’service exceptions used by the VES Event Listener API are defined below.
MessageId |
Description / Comment |
Text |
Variables |
Parent HTTP Code |
|---|---|---|---|---|
SVC0001 |
General service error (see SVC2000) |
<custom error message> |
None |
400 |
SVC0002 |
Bad parameter |
Invalid input value for message part %1 |
%1: message part |
400 |
SVC1000 |
No server resources |
No server resources available to process the request |
None |
500 |
SVC2000 |
More elaborate version of SVC0001 |
The following service error occurred: %1. Error code is %2. |
%1: human readable description of the error %2: error code |
400 |
Table - Service Exceptions
8.53. Policy Exceptions
When a service is not able to complete because the request fails to meet a policy criteria, then the service will issue a fault using the policy exception fault message. To clarify how a policy exception differs from a service exception, consider that all the input to an operation may be valid as meeting the required input for the operation (thus no service exception), but using that input in the execution of the service may result in conditions that require the service not to complete. Examples of policy exceptions include privacy violations, requests not permitted under a governing service agreement or input content not acceptable to the service provider.
A Policy Exception uses the letters ‘POL’ at the beginning of the message identifier. ‘POL’policy exceptions used by the VES Event Listener API are defined below.
MessageId |
Description / Comment |
Text |
Variables |
Parent HTTP Code |
|---|---|---|---|---|
POL0001 |
General policy error (see POL2000) |
A policy error occurred. |
None |
401 |
POL1009 |
User not provisioned for service |
User has not been provisioned for service |
None |
401 |
POL1010 |
User suspended from service |
User has been suspended from service |
None |
401 |
POL2000 |
More elaborate version of POL0001 |
The following policy error occurred: %1. Error code is %2. |
%1: human readable description of the error %2: error code |
401 |
POL9003 |
Message size exceeds limit |
Message content size exceeds the allowable limit |
None |
400 |
Table - Policy Exceptions
8.54. REST Operation Overview
8.54.1. REST Operation Summary
Operation Action |
HTTP Verb |
Resource URL relative to {ServerRoot}, which is defined in section 3 |
publishAnyEvent |
POST |
/eventListener/v{apiVersion} |
publishEventBatch |
POST |
/eventListener/v{apiVersion}/eventBatch |
Table - REST Operation Summary
8.54.2. API Version
apiVersion is used to describe the major version number of the event listener API (which is the same as the major version number of this specification). When this number changes, the implication is: clients of older versions will break in some way, if they try to use the new API without modification (e.g., unmodified v1 clients would not be able to use v2 without error).
8.54.3. Buffering of Events
{ServerRoot} is defined in section 3 of this document, which defines the REST resource URL. One or more FQDNs may be provisioned in an event source when it is instantiated or updated. If an event source is unable to reach any of the provisioned FQDNs, it should buffer the event data specified below, up to a maximum of 1 hour, until a connection can be established and the events can be successfully delivered to the VES Event Listener service.
During such an outage, only the following events should be buffered:
Faults with eventSeverity of “MINOR”, “MAJOR” or “CRITICAL”
Syslogs with syslogSev of 0-5
All MeasurementsForVfScaling events
VNFs acting as event sources should not send syslog events to the VES Event Listener during debug mode (which is controlled via the Netconf management interface), but should store syslog events locally for access, and possible FTP transfer, via the VNF console (e.g., command line interface).
If the internal event source event buffer or local storage should overflow, then the event source should send a Fault event, and should discard events in a first-in, first-out (FIFO) manner (i.e., discard oldest events first).
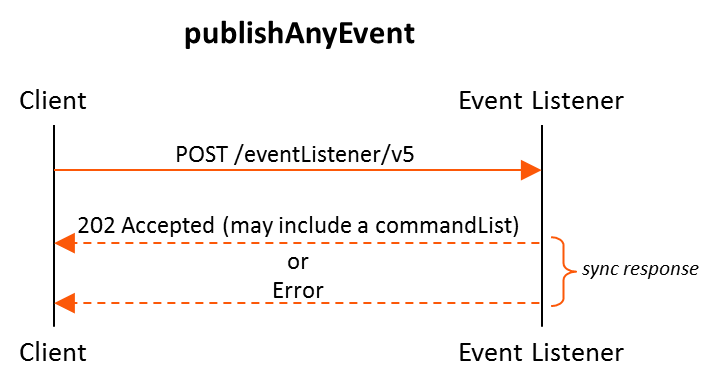
8.55. Operation: publishAnyEvent
8.55.1. Functional Behavior
Allows authorized clients to publish any single event to the VES event listener.
Supports only secure HTTPS (one way SSL) access.
Uses the HTTP verb POST
Supports JSON content types
Provides HTTP response codes as well as Service and Policy error messages
8.55.2. Call Flow
Figure 2 - publishAnyEvent Call Flow
8.55.3. Input Parameters
Header Fields (note: all parameter names shall be treated as case-insensitive):
Parameter |
Data Type |
Required? |
Brief description |
Accept |
string |
No |
Determines the format of the body of the response. Valid values are:
|
Authorization |
string |
Yes |
The username and password are formed into one string as “username:password”. This string is then Base64 encoded to produce the encoded credential which is communicated in the header after the string “Authorization: Basic “. See examples below. If the Authorization header is missing, then an HTTP 400 Invalid Request message shall be returned. If the string supplied is invalid, then an HTTP 401 Unauthorized message shall be returned. |
Content-length |
integer |
No |
Note that content length is limited to 1Megabyte. |
Content-type |
string |
Yes |
Must be set to one of the following values:
|
Body Fields:
Parameter |
Data Type |
Required? |
Brief description |
Event |
event |
Yes |
Contains the JSON structure of the common event format. |
8.55.4. Output Parameters
Header fields:
Parameter |
Data Type |
Required? |
Brief description |
Content-length |
integer |
No |
Used only in error conditions. |
Content-type |
string |
No |
Used only in error conditions |
Date |
datetime |
Yes |
Date time of the response in GMT |
Body Fields (for success responses): no content is provided and the header fields are not required.
Body Fields (for error Responses):
Parameter |
Data Type |
Required? |
Brief description |
requestError |
requestError |
Yes (for errors) |
Used only in error conditions. |
8.55.5. HTTP Status Codes
Code |
Reason Phrase |
Description |
|---|---|---|
202 |
Accepted |
The request has been accepted for processing |
400 |
Bad Request |
Many possible reasons not specified by the other codes (e.g., missing required parameters or incorrect format). The response body may include a further exception code and text. HTTP 400 errors may be mapped to SVC0001 (general service error), SVC0002 (bad parameter), SVC2000 (general service error with details) or PO9003 (message content size exceeds the allowable limit). |
401 |
Unauthorized |
Authentication failed or was not provided. HTTP 401 errors may be mapped to POL0001 (general policy error) or POL2000 (general policy error with details). |
404 |
Not Found |
The server has not found anything matching the Request-URI. No indication is given of whether the condition is temporary or permanent. |
405 |
Method Not Allowed |
A request was made of a resource using a request method not supported by that resource (e.g., using PUT on a REST resource that only supports POST). |
500 |
Internal Server Error |
The server encountered an internal error or timed out; please retry (general catch-all server-side error).HTTP 500 errors may be mapped to SVC1000 (no server resources). |
8.55.6. Sample Request and Response
8.56. Sample Request
POST /eventListener/v5 HTTPS/1.1 Authorization: Basic QWxhZGRpbjpvcGVuIHNlc2FtZQ== content-type: application/json content-length: 12345 { "event": { "commonEventHeader": { "version": 3.0, "domain": "fault", "eventName": Fault\_MobileCallRecording\_PilotNumberPoolExhaustion", "eventId": "ab305d54-85b4-a31b-7db2-fb6b9e546015", "sequence": 0, "priority": "High", "reportingEntityId": "cc305d54-75b4-431b-adb2-eb6b9e541234", "reportingEntityName": "EricssonOamVf", "sourceId": "de305d54-75b4-431b-adb2-eb6b9e546014", "sourceName": "scfx0001vm002cap001", "nfNamingCode": "scfx", "nfcNamingCode": "ssc", "startEpochMicrosec": 1413378172000000, "lastEpochMicrosec": 1413378172000000 }, "faultFields": { "faultFieldsVersion": 2.0, "alarmCondition": "PilotNumberPoolExhaustion", "eventSourceType": "other", "specificProblem": "Calls cannot complete - pilot numbers are unavailable", "eventSeverity": "CRITICAL", "vfStatus": "Active", "alarmAdditionalInformation": [ { "name": "PilotNumberPoolSize", "value": "1000" } ] } } }
8.57. Sample Success Response #1
HTTPS/1.1 202 Accepted
Sample Policy Exception
HTTPS/1.1 400 Bad Request content-type: application/json content-length: 12345 Date: Thu, 04 Jun 2009 02:51:59 GMT { "requestError": { "policyException": { "messageId": "POL9003", "text": "Message content size exceeds the allowable limit", } } }
HTTPS/1.1 400 Bad Request content-type: application/json content-length: 12345 Date: Thu, 04 Jun 2009 02:51:59 GMT { "requestError": { "serviceException": { "messageId": "SVC2000", "text": "Missing Parameter: %1. Error code is %2" "variables": [ "severity", "400" ] } } }
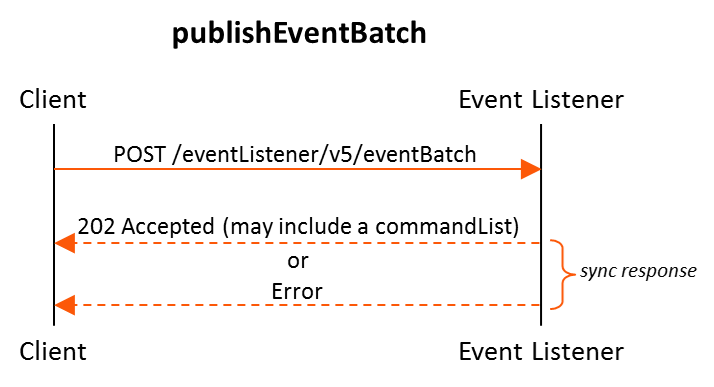
8.58. Operation: publishEventBatch
8.58.1. Functional Behavior
Allows authorized clients to publish any single event to the VES event listener.
Supports only secure HTTPS (one way SSL) access.
Uses the HTTP verb POST
Supports JSON content types
Provides HTTP response codes as well as Service and Policy error messages
8.58.2. Call Flow
Figure 3 publishEventBatch Call Flow
8.58.3. Input Parameters
Header Fields (note: all parameter names shall be treated as case-insensitive):
Parameter |
Data Type |
Required? |
Brief description |
Accept |
string |
No |
Determines the format of the body of the response. Valid values are:
|
Authorization |
string |
Yes |
The username and password are formed into one string as “username:password”. This string is then Base64 encoded to produce the encoded credential which is communicated in the header after the string “Authorization: Basic “. See examples below. If the Authorization header is missing, then an HTTP 400 Invalid Request message shall be returned. If the string supplied is invalid, then an HTTP 401 Unauthorized message shall be returned. |
Content-length |
integer |
No |
Note that content length is limited to 1Megabyte. |
Content-type |
string |
Yes |
Must be set to one of the following values:
|
Body Fields:
Parameter |
Data Type |
Required? |
Brief description |
eventList |
eventList |
Yes |
Array of events conforming to the common event format. |
8.58.4. Output Parameters
Header fields:
Parameter |
Data Type |
Required? |
Brief description |
Content-length |
integer |
No |
Used only in error conditions. |
Content-type |
string |
No |
Used only in error conditions |
Date |
datetime |
Yes |
Date time of the response in GMT |
Body Fields (for success responses): no content is provided and the header fields are not required.
Body Fields (for error Responses):
Parameter |
Data Type |
Required? |
Brief description |
requestError |
requestError |
Yes (for errors) |
Used only in error conditions. |
8.58.5. HTTP Status Codes
Code |
Reason Phrase |
Description |
|---|---|---|
202 |
Accepted |
The request has been accepted for processing |
400 |
Bad Request |
Many possible reasons not specified by the other codes (e.g., missing required parameters or incorrect format). The response body may include a further exception code and text. HTTP 400 errors may be mapped to SVC0001 (general service error), SVC0002 (bad parameter), SVC2000 (general service error with details) or PO9003 (message content size exceeds the allowable limit). |
401 |
Unauthorized |
Authentication failed or was not provided. HTTP 401 errors may be mapped to POL0001 (general policy error) or POL2000 (general policy error with details). |
404 |
Not Found |
The server has not found anything matching the Request-URI. No indication is given of whether the condition is temporary or permanent. |
405 |
Method Not Allowed |
A request was made of a resource using a request method not supported by that resource (e.g., using PUT on a REST resource that only supports POST). |
500 |
Internal Server Error |
The server encountered an internal error or timed out; please retry (general catch-all server-side error).HTTP 500 errors may be mapped to SVC1000 (no server resources). |
8.58.6. Sample Request and Response
8.59. Sample Request
POST /eventListener/v5/eventBatch HTTPS/1.1 Authorization: Basic QWxhZGRpbjpvcGVuIHNlc2FtZQ== content-type: application/json content-length: 12345 { "eventList": [ { "commonEventHeader": { "version": 3.0, "domain": "fault", "eventName": "Fault\_MobileCallRecording\_PilotNumberPoolExhaustion", "eventId": "ab305d54-85b4-a31b-7db2-fb6b9e546015", "sequence": 0, "priority": "High", "reportingEntityId": "cc305d54-75b4-431b-adb2-eb6b9e541234", "reportingEntityName": "EricssonOamVf", "sourceId": "de305d54-75b4-431b-adb2-eb6b9e546014", "sourceName": "scfx0001vm002cap001", "nfNamingCode": "scfx", "nfcNamingCode": "ssc", "startEpochMicrosec": 1413378172000000, "lastEpochMicrosec": 1413378172000000 }, "faultFields": { "faultFieldsVersion": 2.0, "alarmCondition": "PilotNumberPoolExhaustion", "eventSourceType": "other", "specificProblem": "Calls cannot complete - pilot numbers are unavailable", "eventSeverity": "CRITICAL", "vfStatus": "Active", "alarmAdditionalInformation": [ { "name": "PilotNumberPoolSize", "value": "1000" } ] } }, { "commonEventHeader": { "version": 3.0, "domain": "fault", "eventName": "Fault\_MobileCallRecording\_RecordingServerUnreachable", "eventId": "ab305d54-85b4-a31b-7db2-fb6b9e546025", "sequence": 0, "priority": "High", "reportingEntityId": "cc305d54-75b4-431b-adb2-eb6b9e541234", "reportingEntityName": "EricssonOamVf", "sourceId": "de305d54-75b4-431b-adb2-eb6b9e546014", "sourceName": "scfx0001vm002cap001", "nfNamingCode": "scfx", "nfcNamingCode": "ssc", "startEpochMicrosec": 1413378172000010, "lastEpochMicrosec": 1413378172000010 }, "faultFields": { "faultFieldsVersion": 2.0, "alarmCondition": "RecordingServerUnreachable", "eventSourceType": "other", "specificProblem": "Recording server unreachable", "eventSeverity": "CRITICAL", "vfStatus": "Active" } } ]}
8.60. Sample Success Response #1
HTTPS/1.1 202 Accepted
Sample Policy Exception
HTTPS/1.1 400 Bad Request
content-type: application/json
content-length: 12345
Date: Thu, 04 Jun 2009 02:51:59 GMT
{
"requestError": {
"policyException": {
"messageId": "POL9003",
"text": "Message content size exceeds the allowable limit",
}
}
}
HTTPS/1.1 400 Bad Request
content-type: application/json
content-length: 12345
Date: Thu, 04 Jun 2009 02:51:59 GMT
{
"requestError": {
"serviceException": {
"messageId": "SVC2000",
"text": "Missing Parameter: %1. Error code is %2"
"variables": [
"severity",
"400"
]
}
}
}